Bloom taxonomy Definition
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that categorizes different levels of learning objectives.
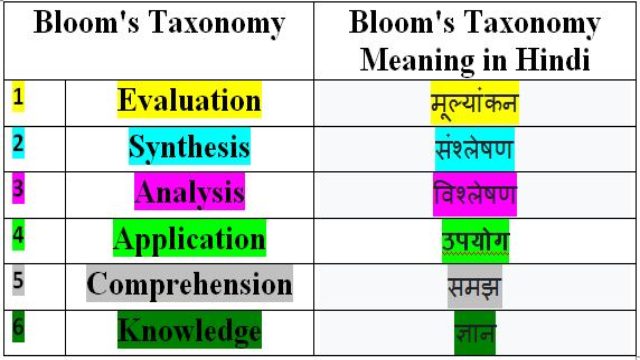
Bloom taxonomy meaning in Hindi
- In Hindi, Bloom’s taxonomy can be translated as “ब्लूम की श्रेणियाँ” (Bloom ki shreniyaan).
- Bloom’s taxonomy is a framework used to classify educational objectives and learning outcomes.
- It was developed by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in the 1950s.
- The taxonomy consists of six levels or categories, organized in a hierarchical manner.
- The six levels, in ascending order of cognitive complexity, are Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
- Each level represents a different type of thinking skill, starting from basic recall and understanding to higher-order thinking and evaluation.
- Educators often use the taxonomy to design learning experiences and assessments that promote higher-order thinking skills.
- It provides a structure for educators to set clear learning objectives and guide the progression of learning activities.
- Bloom’s taxonomy encourages students to move beyond simple memorization and promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
- The taxonomy can be applied to various subject areas and disciplines.
- It is widely recognized and used in educational settings worldwide as a valuable tool for instructional design and assessment.
ब्लूम की श्रेणीबद्धता (Bloom’s Taxonomy) एक ढांचा है जो विद्यालयी शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में विभिन्न स्तरों के शिक्षा उद्देश्यों को श्रेणीबद्ध करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। यह ढांचा बेंजामिन ब्लूम द्वारा विकसित किया गया है।
| Bloom’s Taxonomy Meaning in Hindi | ||
| 1 | Evaluation | मूल्यांकन |
| 2 | Synthesis | संश्लेषण |
| 3 | Analysis | विश्लेषण |
| 4 | Application | उपयोग |
| 5 | Comprehension | समझ |
| 6 | Knowledge | ज्ञान |
Who developed Bloom taxonomy?
Bloom taxonomy was developed by Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist, in the 1950s.
Different levels of Bloom taxonomy
The taxonomy consists of six levels or categories of cognitive skills that learners can demonstrate as they progress in their understanding and application of knowledge. These levels, in ascending order of complexity, are:
Knowledge
This level involves recalling or remembering factual information or concepts.
Comprehension
At this level, learners demonstrate their understanding of concepts by explaining or interpreting them.
Application
Learners apply their knowledge and understanding to solve problems or complete tasks in new or unfamiliar situations.
Analysis
This level involves breaking down complex information into its component parts and examining their relationships.
Synthesis
At this level, learners combine elements or information to create something new, such as generating hypotheses or designing solutions.
Evaluation
The highest level of Bloom’s Taxonomy, evaluation, involves making judgments or assessments based on criteria and evidence.
Detailed Introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy
In the field of education, providing students with a comprehensive and meaningful learning experience is paramount. Educators have long sought effective frameworks and tools to guide instructional design and assessment to achieve this goal. One such framework that has stood the test of time is Bloom’s Taxonomy. Developed by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom in the 1950s, this taxonomy offers a structured approach to categorize and enhance the cognitive skills students acquire during their educational journey. This article explores the significance of Bloom’s Taxonomy in promoting deeper learning and critical thinking.
Understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a hierarchical structure that classifies cognitive skills into six levels. Each level represents an increasingly complex and sophisticated form of thinking. The levels, in ascending order, are Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. Educators can utilize this taxonomy to formulate instructional objectives, design assessments, and scaffold learning experiences.
- Knowledge: At the foundational level of Bloom’s Taxonomy lies Knowledge. This involves the recall of facts, information, and concepts. It requires students to remember and identify key elements, definitions, and details within a subject area. Knowledge serves as the building block upon which higher-level cognitive skills are developed.
- Comprehension: Moving beyond the mere recall of information, Comprehension requires students to understand and interpret concepts. This level involves grasping the meaning, organization, and relationships among ideas. Students demonstrate comprehension by explaining, summarizing, or paraphrasing information in their own words.
- Application: Application takes learning to the next level by enabling students to apply their knowledge and understanding to real-world situations. This level focuses on problem-solving and the transfer of knowledge to novel contexts. Students are challenged to utilize their acquired knowledge to analyze and solve problems, make connections, and propose solutions.
- Analysis: Analysis entails breaking down complex information into constituent parts and examining their relationships. This level fosters critical thinking skills by encouraging students to identify patterns, analyze components, and determine cause-and-effect relationships. Students are expected to engage in a deeper exploration of ideas, distinguishing between relevant and irrelevant information.
- Synthesis: Synthesis involves combining knowledge, ideas, or elements to create something new. At this level, students are challenged to generate hypotheses, design solutions, or create original works. It promotes creativity, problem-solving, and the integration of disparate concepts to construct a holistic understanding of the subject matter.
- Evaluation: Evaluation, the highest level of Bloom’s Taxonomy, requires students to make judgments and assessments based on criteria and evidence. It involves critically analyzing information, arguments, or theories to form reasoned opinions or conclusions. Students engage in higher-order thinking by evaluating the validity, reliability, and effectiveness of ideas or solutions.
Benefits of Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Bloom’s Taxonomy offers several benefits in educational settings.
- It encourages educators to design instructional activities that progressively challenge students, promoting more profound levels of thinking and understanding.
- By aligning assessments with the taxonomy, educators can evaluate students’ mastery of cognitive skills and tailor their instruction accordingly.
- Moreover, Bloom’s Taxonomy cultivates critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and independent learning—essential skills for success in the 21st-century world.
Final Thoughts
Bloom’s Taxonomy serves as a powerful framework for educators to foster deeper learning, critical thinking, and skill development among students. By guiding instructional design and assessment practices, it encourages educators to move beyond surface-level knowledge and engage students in higher-order thinking tasks.
We hope that the content regarding bloom taxonomy meaning in hindi was helpful and knowledgeable for you. For more translation in hindi, keep checking our hindi meaning category.
Embracing Bloom’s Taxonomy empowers educators to create a rich and transformative learning environment that equips students with the cognitive tools they need to thrive in an ever-evolving world.